Abstract
Industrial pollution is the contamination of the
environment by businesses, particularly plants and factories, that dump waste
products into the air and water. Industrial waste is one of the largest
contributors to the global pollution problem endangering people and the
environment.
Environmental pollution is as old as the civilization itself. It has become a major concern in the last few decades. It is the by-product of the development of civilization and in fact a price for the progress. Necessary steps are to be taken to protect the environment for our own existence. This paper provides an overview of the industrial pollution, types of industrial pollution, causes of industrial pollution, impacts of industrial pollution and the ways to manage industrial pollution with respect to Bangladesh environmental policy.
Environmental pollution is as old as the civilization itself. It has become a major concern in the last few decades. It is the by-product of the development of civilization and in fact a price for the progress. Necessary steps are to be taken to protect the environment for our own existence. This paper provides an overview of the industrial pollution, types of industrial pollution, causes of industrial pollution, impacts of industrial pollution and the ways to manage industrial pollution with respect to Bangladesh environmental policy.
Introduction
Pollution has become the first
enemy of the mankind. Industrial revolution of 19th century led to
environmental disaster. Industrial pollution is pollution which can be directly
or indirectly linked with industry, in contrast to other pollution sources. With
the process of industrialization comes our social change, economic development,
and technological innovation. But knowingly or unknowingly we are introducing
another entity to the civilization, it’s industrial pollution. Industrial
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that
causes instability, disorder, harm, or discomfort to the ecosystem. This is one
of the leading causes of pollution worldwide.The Bangladesh Environment
Protection Act, 1995 defines pollution as: An Act made to protect the
environment, to improve the quality of the environment and to control and abate
the pollution of the environment. The whole world is now more afraid of
pollution rather than nuclear blast. Technological advancement has brought
revolutionary changes in life style and national economy with overwhelming
power over nature. The protection of environment has become a major issue
around the global for the wellbeing of the people and economic development.The
present environmental condition of Bangladesh is not at all equilibrium. Severe
air, water and noise pollution are threatening human health, ecosystems, and
economic growth of Bangladesh. Air pollution caused due to increasing
population, burning fossil fuels, industrialization, and associated
motorization. The water pollution caused due to industrialization. The
underground water of Bangladesh has been polluted due to arsenic. Environmental
degradation of Bangladesh is also caused due to poverty, over-population, and
lack of awareness on the subject.The government has taken few steps to improve
the environmental degradation and pollution control. This paper analyzes the
different types of environmental pollution and associated health hazard in
Bangladesh. It also discusses the different governmental steps as well as some
suggested steps to improve the pollution control.
1. Types
of Industrial Pollution
1.1.Air Pollution
Air pollution is a serious environmental health
hazard affecting the populations of Bangladesh. Air pollution of Bangladesh is caused
due to increasing population and associated motorization.Air pollution occurs when different
toxic gases like Sulpher Di Oxide, carbon Di Oxide, Nitrogen Di Oxide etc. get
emitted from different industries and mix with atmosphere and cause environmental
hazard.
Table
– 1: Bangladesh National Ambient Air Quality Standards
Table – 2:
Pollutants in the Air of Dhaka City
Table – 3:
Pollutants in the Air of Dhaka City
Source: Department of Environment (DOE), 1997.
Industrial
Discharge
Industries
cause air pollution through smoke emission. Agro based industries like sugar,
pulp, paper, tanneries and value added industries like textile, garments,
pharmaceutics, oil refineries, fertilizer and chemical industries are the major
contributors for air pollution.
Table-4:
Air Pollution Percentage of most Five Industrial Sectors of Bangladesh in the
Year 2001
Source: Research
Work by Islam Faisal on “Industrial Pollution in Bangladesh” in the year 2002.
1.2.Water
Pollution
Water
pollution is caused by emission of domestic or urban sewage, agricultural
waste, and industrial effluents into water bodies. Nowadays, one of the main
sources of water pollution is the waste material discharged by industrial
units, known as industrial water pollution.The main industrial
areas of Bangladesh are at Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna, and Bogra districts. The
mostly contributing industries for water pollution are pulp and paper,
pharmaceuticals, metal processing, food industry, fertilizer, pesticides,
dyeing and painting, textile, tannery etc. More than 200 rivers of Bangladesh
directly or indirectly receive a large quantity of untreated industrial wastes
and effluent. Everyday approximately 700 tanneries of Dhaka city are
discharging about 16,000 cubic meters of toxic wastes. The Department of
Environment (DOE) has listed 1,176 factories that cause pollution throughout
the country.
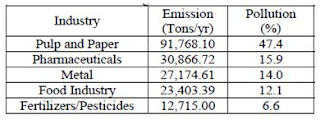
Table-5:
Water Pollution Percentage of most Five Industrial Sectors of Bangladesh in the
Year 2001
Source:
Research Work by Islam Faisal on “Industrial Pollution in Bangladesh” in the
year 2002.
1.3.Soil Pollution
Large quantity of solid wastes like unused and rejected
chemicals (calcium carbonate, magnesium sulphate, fly ashes & bottles)
unwanted industrial wastes generated (rejection, plastic or wooden solids) are
dumped over on the surface of soil by almost all industries with difference in
degree.
1.4.Noise Pollution
Industrial noise is usually considered mainly from the point
of view of environmental health and safety, rather than nuisance, as sustained
exposure can cause permanent hearing damage and raises systolic blood pressure.According
to World Health Organization (WHO), 60 decibel (DB) sound can make a man deaf
temporarily and 100 DB sound can cause complete deafness. According to the
Department of Environment (DOE), the perfect sound condition for Bangladesh is
45 dB for the daytime and 35 dB for the night in peaceful areas and 50 dB for
the daytime and 40 dB for the night in residential areas. The main sources of
noise pollution are industries, motorized vehicles, construction works and
indiscriminate use of loudspeaker. At present noise level in Dhaka city are
estimated ranging from 60 to 100 decibels. If present situation continues then
by the year 2017, 50% people of Dhaka city will loss 30 decibelsof hearing
power.
Table – 6: Pollutants
in the Air of Dhaka City.
Source:
Nazmul Chowdhury research on noise pollution in Dhaka city on Feb 2002.
1.5.Oil Pollution
An oil spill is a release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon
into the environment due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The
term often refers to marine oil spills, where oil is released into the ocean or
coastal waters.
1.6.Nuclear Pollution
It is a new form of Industrial pollution which has been seen
in the recent centuries. Nuclear pollution takes place in the form of
radioactivity evolved from radioactive wastes from nuclear reactors. Like,
Nuclear Bomb, War etc.
2. Causes
of Industrial Pollution
There is so many causes for pollution, we are taking some
major causes.
2.1.Textile Mills
They use different kinds of chemicals in different stages,
Like, dyeing of cotton, silk, PVC & synthetic etc. About 5000 garment
industries exist in Bangladesh. Waste from BSCIC Industrial Area in Gazipur
ends up in the BaimailJheel and then flows into the Turag turning water of both
into an obnoxious deep purple liquid. The garments industries and textile
industries are creating a huge number of Chloro-Fluoro-Carbon, Which is
extensive cause of Air Pollution.
2.2.Chemical wastes from Pharmaceuticals
During the production processes in pharmaceutical
industries, various hazardous and nonhazardous products are dumped which
ultimately ends up in the rivers surrounding the industries causing intolerable
stench and renders the water unusable for any domestic purpose.
2.3.Chemical wastes from Tannery
About 300 hundred tannery industries of different sizes and
categories in Bangladesh. One of the main by product in the tanneries is the
Chromium which causes severe water pollution and is harmful for human body.
2.4.Stable Materials Waste
Stable materials waste, as is known, are all sorts of
refuses waste from offices, factories, markets, public institutions or it may come,
some other ways. The estimation for stable materials solid waste production for
Dhaka has varied from 3000 – 4500 metric tons per day. It’s like a thread of
living.
3. Impacts
of Industrial Pollution
Industrial pollution has great impact on the ecological
balance of the atmosphere along with biological impacts in this planet. Some of
these are given bellow.
3.1.Ecological impacts
v Loss of fertility of soil
v Decreases the level of dissolved
oxygen
v Acid Rain
v Global warming
v Environmental hazards
3.2.Biological Impacts
v Endangers the aquatic fauna
v Cause water borne diseases
v Skin Cancer on human beings
v
Respiratory
diseases
Environmental policy
There aresomedefinitions of environmental policy. Those aregiven below-
v Environmental policy refers to the commitment of an
organization
to the laws, regulations, and other policy mechanisms concerning environmental issues and sustainability.
v Environmental policy is the statement by a supranational,
national, or regional
government of its approach to environmental protection.
Overview
of Environmental Policy of Bangladesh
The
first regulation related to environment in Bangladesh was the Factory Act of
1965, which was followed by the earliest recorded environmental protection act,
known as the ‘Water Pollution Control Ordinance, 1970’. However, these
ordinances do not include air pollution problems. Gradually these ordinances
were modified and the Environmental Pollution Control Ordinance (EPC), 1977,
was promulgated. It dealt with pollution of air, surface water and groundwater,
and soil by discharge of liquid, gaseous, solid, radioactive, or other
substances. Although the order passed under the EPC 1977 was legally in place,
implementation of environmental laws never took place.Following rapid industrialization
the environmental scenario in Bangladesh changed dramatically. The Ministry of
Environment and Forest and the Department of Environment were created in 1989
and the Environment Policy of 1992 was introduced. Further, the Environmental
Conservation Act, 1995, and the Environment Conservation Rules, 1997, were
approved by the Bangladesh National Assembly to restrict and mitigate
ever-growing environmental problems in the country.The ‘Ministry of Environment
and Forest (MOEF)’ of Bangladesh is primarily responsible for environmental protection.
The MOEF has taken some steps to control the environmental pollution of
Bangladesh.
Environmental
policy of Bangladesh
Bangladesh National Environment Policy approved in May 1992 sets out the basic framework
for environmental action, together
with
a set of broad sectorial action guidelines.
The objectives of Environment Policy are to
v Maintain
ecological balance and overall development through protection
v Improvement
of the Environment
v Protect
the country against disaster
v Identify
and regulate the activities which pollute and degrade the Environment
v Ensure
Environmentally sound development in all sectors
v Ensure
sustainable and long term environmentally sound use of all national resources
v Actively
remain associated all international environmental initiatives to the maximum
possible extent.
Environmental policy of Bangladesh
addressed 15 broad sectors to address overall environmental issues. From these
sectors, industrial sector considered one of the most threatened sector for environmental
pollution.
Industrial
Sector
v Step
by step, adopting corrective measures against industries polluting the
environment
v Ensure
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) in establishing all new industries both
public and private sectors
v Impose
ban on establishment of industries producing goods which cause environmental
pollution; close down such existing industries gradually and discourage use of
such polluting products through development/ introduction of their substitutes
which are environmentally sound.
v Encourage
development of environmentally sound and appropriate technology and initiatives
on research and extension in the fields of industry . Balance such initiatives
with the best use of labor and provision of proper wages.
v Prevent
wastage of raw materials in industries and ensure the sustainable use.
Action plan
v Industries
identified by the Department of Environment will take pollution control
measures as soon as possible
v Industries
that are potential polluters will make provisions to introduce pollution
control measures
v Steps
will be taken to shift the industries located in residential area to
appropriate locations. Planned industrial zones will be delineated.
v Industries
using heavy metal such as mercury, chromium, lead, etc. will be initially discouraged
and finally prohibited.
v Polluting
industries will install their own polluting monitoring devices
v To
facilitate waste disposal management, waste permit/consent order, system will
be established in the industrial sector.
v Recycling
will be encouraged.
Industrial Effluent Discharge
v Numerous textile and tannery
industries in Bangladesh
v Required to have ETP
v Expensive to treat effluent
v Owners reluctant to spend money on
non-productive issues such as ETP
v Engineers tend to compromise with
the owners
v Technology to treat textile dye may
not always be economically viable
v Buyers and consumers expect good
governance & implementation of rules
v Enforcement of regulations
inadequate in the past; at present more strictly enforced
Recommendation
v Policy Strategy
v Establishment of Special Economic
Zones Based on the Importance of the industries, Availability of Regional
Facilities
v Investment Criteria of Feasibility
Study for Planned Industrialization
v Industrial Technology
v Technical and Institutional
Assistance
v Implementation, Monitoring, and
Review
Conclusion:
It is a challenge for Bangladesh to design and implement an environmental policy
which can address both economic progress and environmental protection. On the other hand,frequent
incidence of pollution added new dimension to the necessity
of having effective environmental
policy to protect the environment. Environment policy should address all the major environment related issues and all
these issues should be addressed properly. If the environment policy
of Bangladesh addressed all
the major concern issues properly, then it will be examined by
comparing this policy
with the policy of the developed countries. If the environment policy of Bangladesh does not address all the major concern issues to manage industrial pollution as well
as other pollutions, then apparently, the environment policy
of Bangladesh should be
reviewed. Good governance in every sector is essential to ensure
ethical management of the environment.Communication between the professionals
and policy makers-end users provides the key to success.
References
v Md Mahbubur
Rahman, “Environmental Pollution in Dhaka City and It’s Effects on Public
Health”, 2003.
v KM Nurul Huda,
“Air Quantity Management Policy and Vehicle Emission Control”, 1998.
v Tariq Bin
Yousuf, “Solid Waste and Sewerage Disposal of Dhaka”, 1998.
v Nazmul Chowdhury,
“Noise pollution in Dhaka city”, 2002.
v Islam Faisal,
“Industrial Pollution in Bangladesh”, The World Bank Dhaka office, 2001.